How Credit Card Interest Works: Methods, Factors, and Tips to Understand APR

Have you ever wondered how is credit card interest charged? This question often appears when your monthly statement arrives and the balance is suddenly higher than expected. Understanding how APR works can make a significant difference in how much you actually pay. In this guide, we will break down the math behind credit card interest, explain the different APR types, and examine the factors that influence your rates. With this knowledge, you’ll be able to use your credit card more wisely and avoid unnecessary debt.
Understanding Credit Card Interest
Before diving deeper, let’s address the fundamental question, “What is credit card interest?” To put it simply, credit card interest is charged by a financial institution for borrowing money. This fee is calculated as a percentage of your outstanding balance and is added to your account regularly. If you carry a balance from month to month, you will be charged interest. If you don’t pay the balance in full, interest continues to accumulate, and over time this can significantly increase your debt.

Does credit card interest accrue daily? In most cases, interest accrues daily, but you are charged monthly. The interest rate is expressed as an Annual Percentage Rate (APR). It is a standardized figure that reflects the yearly cost of borrowing, including interest and certain service fees. As such, APR makes it easier to compare different credit card products.
However, APR is not a single number. There are different types of APR depending on how you use your card: purchase APR (applies to everyday transactions), balance transfer APR (applies when you transfer existing debt to another card), and cash advance APR applies when you withdraw cash from your credit card (usually much higher). Each type can influence how much interest you pay, depending on your spending habits.
Introductory APR
Some credit cards offer an introductory APR to attract new customers. This temporary rate is usually much lower than the standard APR and can apply for 6 to 12 months (sometimes more, depending on the issuer).
When you try to figure out how credit card interest works, make sure you are aware of the effective period of the introductory APR, since the transition to standard interest rates can significantly change the amount of interest you’ll pay on outstanding balances.
Credit Card Interest Calculation Methods
Minimum interest rates will largely depend on how credit card interest is calculated by a particular financial institution. More often than not, you can find a credit card interest calculator on your bank or credit company’s website. While it shows the monthly repayment amounts based on your outstanding balance, it does not explain how the interest is actually calculated.
Most banks use three main methods to determine their interest rate formulas. If you're asking, “How does interest work on a credit card?” these calculations will help you understand the process.
Average Daily Balance Method
This is the most common method used by financial institutions. The bank calculates the average of your daily balances over a billing cycle. For example, how does credit card interest work if you have a 30-day billing cycle with daily balances of $100, $200, $150, and $50? The average daily balance would be: (100 + 200 + 150 + 50) / 30 = $5.67. This average is then multiplied by the card’s daily interest rate and the number of days in the billing cycle. To find the daily interest rate, you divide the APR by 365.
Daily Balance Method
With this method, interest is calculated daily based on the outstanding balance. For example, if your balance is $1,000 and the daily interest rate is 0.03%, the interest for that day would be: $0.30 (1,000 * 0.0003).
Adjusted Balance Method
This approach considers the balance at the beginning of the billing cycle and subtracts any payments or credits made during the period. For instance, if you begin the billing cycle with a $1,000 balance and make a $200 payment, the adjusted balance for interest becomes $800.
An important thing to mention when explaining interest calculations is the grace period. This is a window between the end of a billing cycle and the payment due date. If you pay everything you owe to the bank within this period, you can avoid credit card interest completely. Choosing a card with a favorable grace period can help you manage your balances more efficiently.
Factors Impacting Credit Card Interest Charges
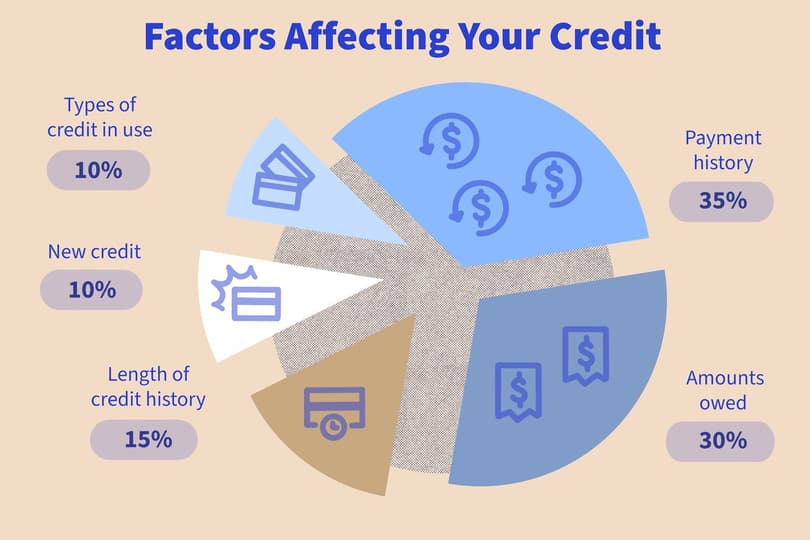
What factors determine the interest banks charge on credit cards? Beyond your APR and outstanding balance, several additional factors influence how much interest you’ll pay once you carry a balance beyond the grace period.
Billing Cycle Length
The length of your billing cycle affects how long your balance accrues interest. A shorter billing cycle means less time for interest to accumulate, which can potentially reduce your charges.
Payment History
Late or missed payments can trigger penalty APRs, which are significantly higher than standard APRs. Maintaining a consistent history of on-time payments is essential to avoiding these costly rates.
Compound Rates
Credit card interest often compounds, meaning new interest may be calculated on top of previously accrued interest. This increases the total amount you owe, making it especially important to pay down your balance consistently.
Creditworthiness
Your credit score and credit history play a major role in how does interest on a credit card work. Borrowers with higher credit scores typically qualify for lower APRs, while those with lower scores may face higher rates due to increased lending risk.
Final Thoughts
Credit cards can be powerful financial tools when you understand how they work. If you know how APR is calculated, what influences your rate, and how daily compounding affects your balance, you’ll be able to manage your debt far more efficiently. A little knowledge goes a long way and can save you a substantial amount of money over time.



![What is the APR on a Credit Card? [How Does it Work?]](https://rates.fm/static/content/thumbs/385x210/d/bc/wun2sw---c11x6x50px50p--086c69113753a543a7475ce8b11c3bcd.jpg)
