Credit Card Interest: What You Need to Know

When searching for a suitable credit card, it’s crucial to fully understand the credit terms you are eligible for. This will ensure that you won’t get into debt and can return the money you owe to the bank without any problems.
All the nuances associated with interest charges can be confusing. Does credit card interest accrue daily? How is credit card interest charged? Here, you will find answers to these and other questions concerning credit card interest.
UNDERSTANDING CREDIT CARD INTEREST
What is credit card interest? Before we proceed with details, let’s answer this question. To put it simply, you are charged a fee by financial institutions for borrowing money from them. This fee is calculated as a percentage of your outstanding balance and is added to your account on a regular basis. If you use a credit card and carry a monthly balance, you will have to pay interest. If you don’t, it will continue to accumulate, and you can end up in debt.

Though typically accrued every month, an interest rate is commonly outlined as an annual percentage rate or APR. It represents the total cost of borrowing annually, including both interest and any applicable service fees. As such, the APR provides a standardized way to compare the costs of different credit card offers.
When evaluating credit card APRs, it’s important to distinguish between purchase APR, balance transfer APR, and APR on cash advances accordingly. Each type may vary, impacting the cost of respective transactions. Knowing specific interest rates associated with different activities will help you get the most out of your credit funds without excess charges.
Introductory APR
Credit card companies might add an introductory APR to attract potential cardholders. This special rate is lower than the standard APR and may be applicable for a limited period, usually six months to a year after opening an account.
When you try to figure out how credit interest works, make sure you are aware of the effective period of the introductory APR since the transition to standard interest rates can significantly alter the amount of interest you will have to pay on outstanding balances.
Credit Card Interest Calculation Methods
So, how credit card interest is calculated? Minimum interest rates will largely depend on the calculation method used by the financial institution. More often than not, you can find a credit card interest calculator on the bank or credit company website. While showing you the due repayment amounts you owe monthly based on the outstanding balance, it doesn’t explain how the interest is actually calculated.
Most banks use two main methods for creating their interest rate formulas. If you ask, “How does interest work on a credit card?” these methods will help you figure it out.
Average Daily Balance Method
This is the most common method used by financial institutions. With this method, the bank calculates the average of your daily balances over a billing cycle. How does credit card interest work if you have a 30-day billing cycle with the following daily balances: $100, $200, $150, and $50? The average daily balance is calculated as (100 + 200 + 150 + 50) / 30 = $5.67. This average is then multiplied by the card’s daily interest rate and the number of days in the billing cycle to determine the interest charges. Then, all there is left to do is to divide the APR by 365 days in a year.
Daily Balance Method
In this approach, interest is calculated daily based on the outstanding balance. How do credit card interests work here? For example, if your balance is $1,000 and the daily interest rate is 0.03%, the interest for the day would be $0.30 (1,000 * 0.0003).
Adjusted Balance Method
It considers the balance at the beginning of the billing cycle and subtracts any payments or credits made during that period. For instance, if you begin the billing cycle with a $1,000 balance and make a $200 payment, the adjusted balance for interest calculation would be $800.
Note: An important thing to mention when explaining interest calculations is a grace period. This is a window between the end of a billing cycle and the due date for the payment. By paying off everything you owe to the bank within this period, you can avoid credit card interest. By choosing a card with a favorable period, you’ll be able to manage your balances more efficiently.
Factors Impacting Credit Card Interest Charges
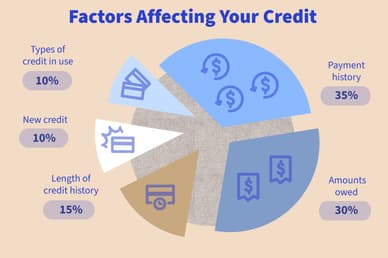
What factors determine the interest banks charge on credit cards? APR and outstanding balance aside, several other factors are taken into account when determining the interest amount you’ll pay on your credit card balance outside the grace period.
Billing Cycle Length
The length of your billing cycle affects the amount of time your balance accumulates interest. A shorter billing cycle means less time for interest to accrue, potentially reducing your charges.
Payment History
Late or missed payments can trigger penalty APRs, which are significantly higher than standard APRs. Maintaining a consistent history of on-time payments is crucial to avoiding these punitive rates.
Compound Rates
Credit card interest often compounds, meaning the percentage won’t always be the same but, in fact, is impacted by any accrued interest from previous months. This compounds the amount you owe, making it crucial to pay down your balance promptly.
Creditworthiness
You should pay a great deal of attention to your credit score and credit history, as they play a huge role in “How does interest on a credit card work?” Individuals with higher credit scores and, therefore, who are more likely to pay off in time typically qualify for lower APRs, while those with lower scores may face higher rates.
Final Thought
Understanding how credit card interest rates are calculated and accrued will enable you to navigate the world of credit more responsibly. Always remember to check all the terms and conditions of your credit card agreement and other documents you sign with the bank to ensure you comprehend how interest is applied to your account. This knowledge will help you manage your funds smarter and minimize interest.
