Payment Gateway: Everything You Need to Know
Contents

Having an effective and convenient system for ensuring your clients can purchase your products or services is essential. Modern payment gateway services allow you to accept payments from customers safely and quickly. What’s more, this technology is applicable in both online and offline commerce.
In this article, you will learn about the most popular payment gateway types, their features, security considerations, and how you can set one up for your business.
What is a Payment Gateway System?
What is a payment gateway, and how does it work? A payment gateway system is a combination of technical devices and digital solutions needed for organizing a digital or offline all-in-one point of sale. In more detail, an online payment gateway system is a network processing set that connects sellers and buyers to accomplish transactions. In the offline sector, a gateway can be imagined as a POS terminal that connects the bank accounts of a merchant and a customer.
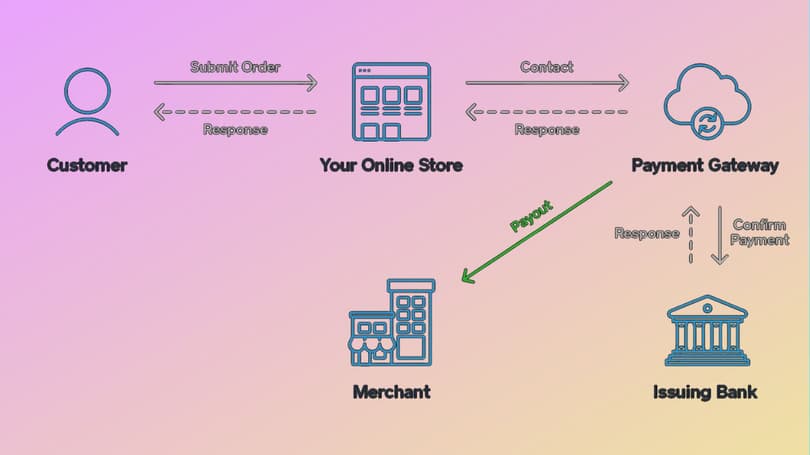
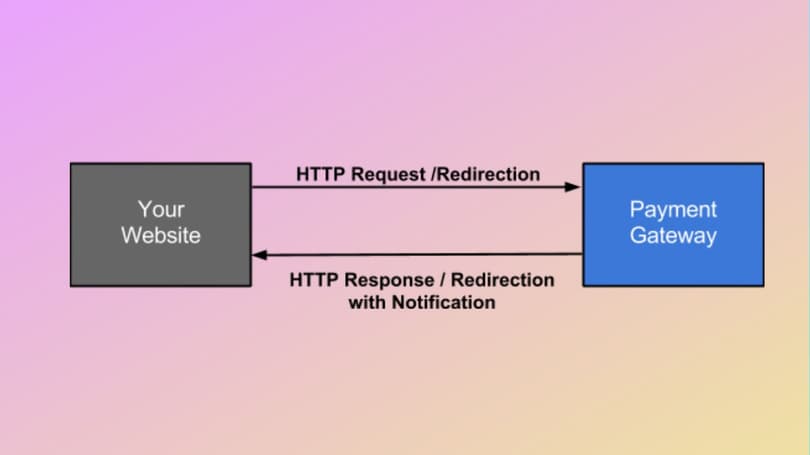
The payment gateway process can be explained by using the scheme presented above. Thus, the Customer visits an online (or offline) Store and starts a procedure. Here, the Payment Gateway receives a request and sends a response to the Issuing Bank (client’s bank) to receive a confirmation of the deal (enough money for a transaction). Then the Payment Gateway makes a payout for a Merchant, sends a deal confirmation back to a website or POS terminal, and informs a Client.
Types of Payment Gateway Systems
To better understand what the process of an online payment gateway is, let’s review four common types of processing. For business owners, it’ll also be helpful as we will explain what this gateway is with examples:
Hosted Payment Gateway
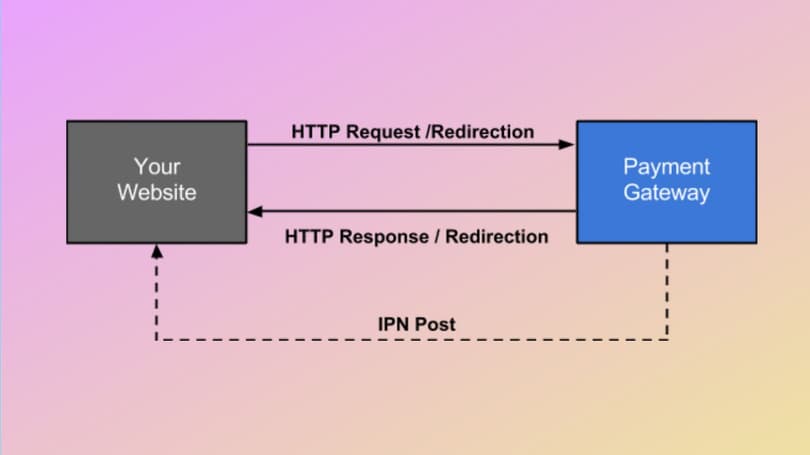
This is one of the simplest but costliest methods of adding a gateway to your online store. It is based on a separate PSP (payment service provider, like PayPal), which redirects clients from your website to a different page and proceeds with the payment. This method benefits from full PCI DSS compliance and fraud protection, with support included in the service cost. The drawbacks include higher fees and transaction rates, alongside limited payment information that can be useful for a merchant.
Self-hosted Payment Gateway
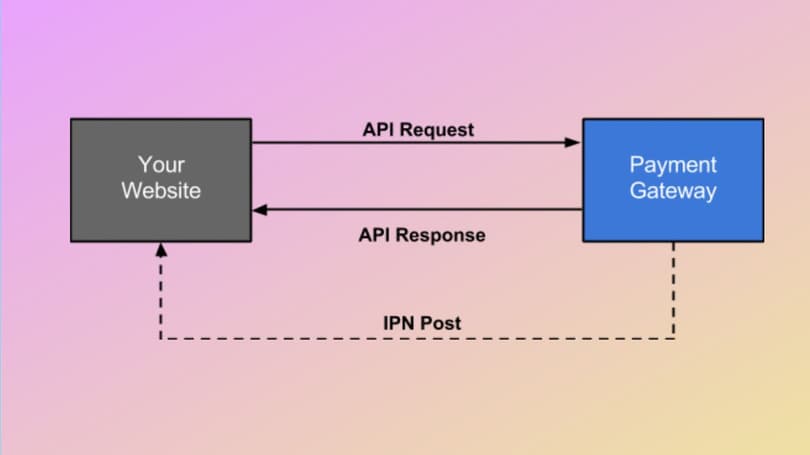
This method looks quite similar to the previous one but with no customers being redirected to external pages. However, you still use an outsourced gateway service (like Shopify). It means organizing the technical processing of the payments on your servers, including protection procedures like encryption. It leads to higher costs spent on technical support, which can be a headache for the merchant. At the same time, it facilitates money processing and simplifies customer payment, giving more info about the client’s journey and reducing fees.
API-hosted Payment Gateway
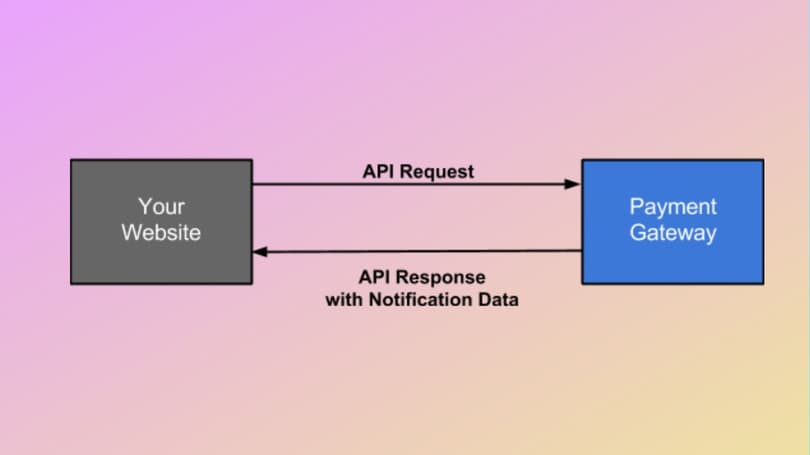
An API-hosted online payment gateway process combines the first two methods, where the client isn’t redirected to additional pages but uses an external processor. However, the merchant should keep data security issues in mind and adjust the API thoroughly so it will work on all the preferred devices. Similar services (Stripe) are usually pretty cheap in terms of fees and fast enough for clients, but they require more time to set up such stripe payment solution.
Local Bank Integration Gateway
Despite being listed at the end, this is the simplest and the most limited way of organizing a gateway on the website. Here, a client’s payment request is redirected to the bank’s gateway, which is then redirected back after the transaction is confirmed. With a pretty simple setup procedure and suitable fees, this method has many drawbacks. This gateway process has limited options (repeating transactions, chargeback), isn’t prepared for scaling up, and has no transaction journey tracking.
Features and Functionality of Payment Gateway Systems
We’ve discussed how payment gateway works and reviewed the major processing features when discovering what the payment gateway service types are. Now, let’s see in detail what functionality the transaction gateway system should have:
Security
This is the most crucial aspect of setting up a gateway. Clients can be disappointed with slow processing or the absence of a specific method. Still, insecure transactions and potential problems may even result in legal issues with significant fines for both merchants and clients.
Processing speed
Merchants should understand both sides of transaction speed. Clients should receive the fastest possible way of closing the deal, while business owners should be able to choose the payment period to the merchant bank account.
Integration
If you have a small business, you may not have additional team members to integrate and support complex transaction gateway systems. Ease of integration, therefore, is the vital aspect, especially for inexperienced merchants who don’t fully understand what a payment gateway account is and how to set it up.
Reports detailing
This is so-called “payment journey tracking.” When you have enough information about refusals, disagreements, or money freeze cases, you can adjust the processing to improve sales.
Payment options
Here, the simple rule “the more, the better” works almost perfectly, as your clients may want to pay in diverse ways. Still, if you are ready to offer them dozens of options, highlight the most widespread ones so as not to confuse the customers (credit and debit card payments, e-wallets, checks, and bonuses).
Setting Up a Payment Gateway System
Now, let’s turn from questions like “How does a payment gateway work?” to more practical issues—how to set up a gateway for your business. The following plan will be valid for small startup-like companies that are focused on online payments:
- Research your business's specifics regarding potential clients and their paying portraits (methods, locations, currencies, etc.).
- Choose the gateway that fits your needs the most—the optimal combination of the above features and functionalities.
- Define specific points your business needs to implement the payment gateway (find an API specialist, set up a server for a self-hosted option, open all needed accounts, create a CRM or specific database, etc.).
- Choose the cooperation plan and start implementation of the functionality of the gateway provider.
- Checkup and test the system, including the speed, fees, and security of connecting payment processors.
- Be ready for some adjustments afterward and leave room for maneuvering.
- Use and test the gateway in battlefield conditions.
Security Considerations for Payment Gateway Systems
Now that you know about payment gateway options and their features, it’s also important to pay attention to the security aspect. Independently of what payment gateway providers offer and their authority, business owners should know basic terms in the security sector:
PCI DSS Compliance
The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards, or PCI DSS, is the cornerstone for all gateways. It refers to international rules requiring a strict protocol for processing banking cards that excludes potential sensitive data leakage.
Encryption and Tokenization
With both terms referring to data protection, they are still quite different. Tokenization stands for replacing sensitive banking info with a token, which is an identifier (or the key) that helps to “understand” the code. Encryption means the same approach where the needed info exists in the hidden code, which must be further decrypted to access.
Address Verification System (AVS)
The Address Verification System is aimed at limiting fraud, especially during chargebacks. To accomplish this task, AVS links the info about the card and address to exclude suspicious data substitutions.
3D Secure Authentication
Implemented by two global card giants, Mastercard and Visa, 3D Secure Authentication aims to reduce fraud via two-factor verification. The newer 3DS2 protocol is in action, which uses advanced authentication methods like biometrics and aforementioned tokenization and works worldwide.
Fraud Prevention Measures
Identifying security threats and frauds in time can save you a lot of money and increase clients’ trust in your website. By implementing Fraud Detection and Prevention Systems (FDPS), you can monitor patterns and suspicious activities and prevent fraudulent transactions before they cause harm.
Conclusion
There is no denying that payment gateways make shopping easier for buyers and also ensure a high level of convenience for sellers. At the same time, there is a lot to consider when choosing a payment gateway for your business. This includes security, integration, processing speed, payment options, and more. It is also crucial to test the selected gateway to ensure it works seamlessly in real-life situations.
The good news is that there are plenty of gateways to choose from, regardless of your business type, fee requirements, and other factors.
FAQ
What is a payment system?
A payment system is a set of hardware and software that organizes money transactions between sellers and clients.
How do I choose a payment gateway?
You should choose a payment gateway according to your business specifics, considering factors such as security, transaction fees, payment options, ease of integration, and many others.
How do I set up a payment gateway?
Setting up a payment gateway involves the following steps:
- research your business needs
- choose a suitable gateway
- prepare your business for implementation
- add the system (hiring specialists if needed)
- test it, including real-time sales
How do I integrate a payment gateway?
Integration depends on the payment gateway type and website specifics. Most services require adding programming code to your website so that it can interact with the payment’s API, create payment forms, and ensure a security measures appliance.
Do I need to create a merchant account before adding a gateway?
Yes, having a merchant account is one of the initial steps before starting payment gateway integration, as you will receive your money there.




